In today’s era of environmental consciousness and resource scarcity, finding innovative solutions to manage waste and maximize resource utilization is paramount. Enter briquetting machines, a game-changing technology that enables the conversion of various waste materials into compact, energy-dense briquettes. Let’s delve into the world of briquetting machines, exploring their functionality, applications, and the transformative impact they have on waste management and resource recovery.
Understanding Briquetting Machines
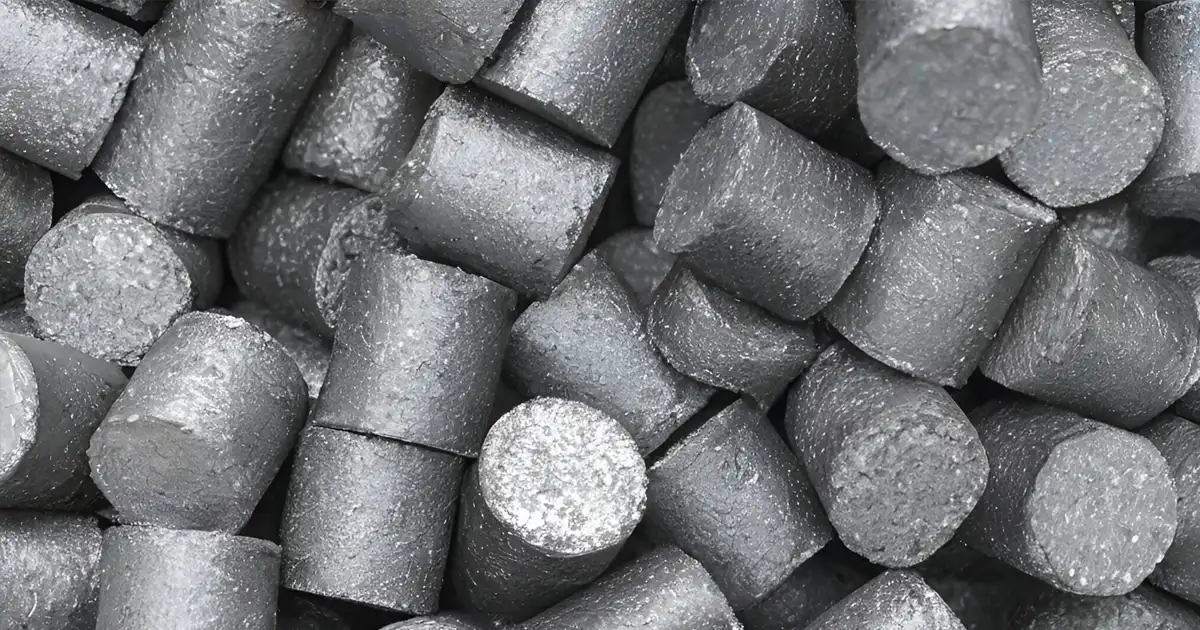
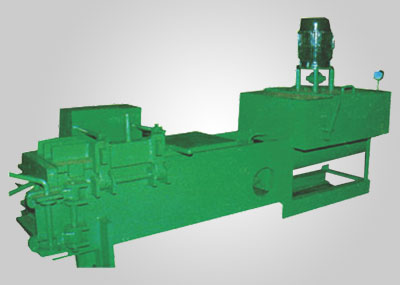
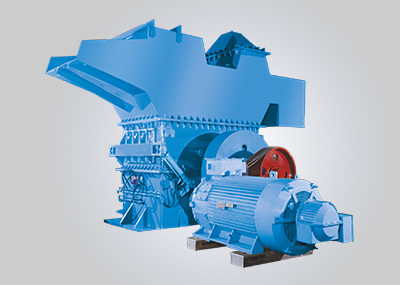
Briquetting machines, also known as briquette presses or briquette makers, are devices designed to compress loose, bulky materials into compact, uniform-sized briquettes. These machines utilize high pressure and mechanical force to bind together fine particles or fibrous materials, transforming them into solid fuel briquettes or densified products suitable for various applications.
How Briquetting Machines Work
The operation of a briquetting machine typically involves the following steps:
- Material Preparation: Raw materials such as biomass residues, agricultural waste, forestry residues, industrial by-products, and other combustible materials are collected and prepared for briquetting. This may involve shredding, chipping, grinding, or drying to achieve the desired particle size and moisture content.
- Feeding: The prepared material is fed into the hopper of the briquetting machine, where it undergoes compression and compaction under high pressure.
- Compression: Inside the briquetting chamber, the material is subjected to intense pressure exerted by hydraulic or mechanical mechanisms. This pressure forces the particles to bind together, forming dense, solid briquettes with high calorific value.
- Briquette Ejection: Once the briquettes reach the desired size and density, they are ejected from the machine and collected for further processing or utilization.
Applications of Briquetting Machines
Briquetting machines find diverse applications across various industries and sectors, including:
- Renewable Energy: Briquettes produced from biomass residues such as wood chips, sawdust, agricultural residues, and municipal solid waste serve as a sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. These biomass briquettes can be used for heating, cooking, and power generation, reducing reliance on non-renewable energy sources and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions.
- Metal Recycling: Briquetting machines are employed in the recycling of metal swarf, chips, and shavings generated from machining operations. By compacting metal waste into briquettes, these machines facilitate easier handling, transportation, and recycling of metal scrap, while also maximizing resource recovery and minimizing environmental impact.
- Waste Management: Briquetting machines play a crucial role in waste management by transforming various types of organic and inorganic waste materials into value-added products. Municipal solid waste, paper sludge, plastic residues, and other waste streams can be briquetted for energy recovery, landfill diversion, or reuse in manufacturing processes.
- Chemical Industry: Briquettes produced from industrial by-products such as coal dust, carbon black, and metallurgical residues find applications in the chemical industry as reductants, catalysts, or additives in manufacturing processes. These briquettes offer cost-effective solutions for waste disposal and resource utilization in chemical production.
Advantages of Briquetting Machines
The adoption of briquetting machines offers numerous advantages, including:
- Waste Reduction: Briquetting machines enable the conversion of waste materials into valuable products, reducing the volume of waste destined for landfills and incineration.
- Resource Conservation: Briquetting promotes resource conservation by utilizing biomass residues, industrial by-products, and other waste materials as feedstock for briquette production, thereby reducing the demand for virgin resources.
- Energy Efficiency: Briquettes serve as a high-energy-density fuel source, offering efficient combustion and heat generation with lower emissions compared to traditional fuels.
- Cost Savings: Briquetting machines help organizations save on waste disposal costs, energy expenses, and raw material procurement, leading to overall cost savings and improved profitability.
Conclusion: Embracing the Briquetting Revolution
In conclusion, briquetting machines represent a transformative technology that holds immense potential for waste management, resource recovery, and sustainable development. By converting waste materials into valuable briquettes, these machines contribute to environmental protection, energy conservation, and circular economy principles. As industries and communities increasingly prioritize sustainability and resource efficiency, the adoption of briquetting machines offers a path towards a cleaner, greener future where waste is no longer seen as a burden but as a valuable resource awaiting transformation.